Overview of Iran’s Air Defense Strategy
Iran’s air defense strategy focuses on countering aerial threats, including ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and drones. The country has invested heavily in developing indigenous systems while also acquiring technology from foreign sources.
Key Air Defense Systems
- Bavar-373
- Description: An Iranian-made long-range surface-to-air missile system, similar to Russia’s S-300.
- Capabilities: Can engage multiple targets, including aircraft and missiles, at a range of up to 200 km.
- Khordad 15
- Description: A mobile air defense system equipped with radar and missiles capable of targeting aircraft and drones.
- Capabilities: Can detect and engage targets up to 150 km away, and is designed to intercept low-flying targets.
- S-300 (Acquired from Russia)
- Description: A long-range air defense system designed to intercept aircraft and missiles.
- Capabilities: Effective against various aerial threats, including ballistic missiles, with a range of around 150 km.
- Talash-3
- Description: A medium-range missile defense system developed by Iran.
- Capabilities: Designed to intercept short-range ballistic missiles and drones.
Effectiveness Against Missile Threats
- Detection and Tracking: Iran has developed radar systems capable of tracking various aerial threats, improving its ability to detect incoming missiles early.
- Integrated Systems: Iran’s air defense strategy includes integrating various systems to create a layered defense, allowing for engagement at different ranges.
- Past Engagements: Iran has claimed success in intercepting drones and missiles, particularly during regional conflicts where it has demonstrated its capabilities, such as during the conflict with Israel and in the Syrian theater.
Challenges
- Technological Limitations: While Iran has made advancements, many of its systems may not match the sophistication of U.S. or Israeli missile defense technologies.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The effectiveness of Iran’s air defense is often tested by regional threats, including potential attacks from Israel or the U.S., which have advanced aerial capabilities.
- Aging Equipment: Some of Iran’s air defense systems are older and may require modernization to effectively counter newer missile technologies.
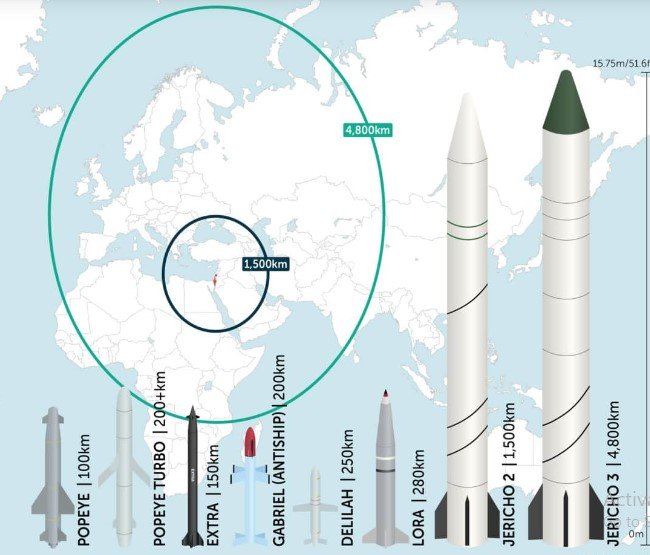
Iran’s Air Defense Systems: Capability to Defend Against Israeli Missile Attacks
Overview
Iran’s air defense systems are designed to counter a range of aerial threats, including potential missile attacks from regional adversaries like Israel. Given the ongoing tensions and historical conflicts, understanding the effectiveness of these systems against Israeli missiles is crucial.
Key Factors in Defending Against Israeli Missile Attacks
- Types of Threats:
- Israel possesses advanced missile systems, including precision-guided munitions, ballistic missiles, and cruise missiles, which are designed to evade detection and interception.
- Iran’s Air Defense Systems:
- Bavar-373: Capable of intercepting various aerial threats, including missiles, with a range of up to 200 km.
- Khordad 15: Designed to engage low-flying targets and missiles at distances up to 150 km.
- S-300: An advanced system acquired from Russia, effective against both aircraft and ballistic missiles, enhancing Iran’s defensive capabilities.
- Layered Defense Strategy:
- Iran employs a multi-layered air defense approach, integrating different systems to provide overlapping coverage. This is intended to increase the chances of intercepting incoming threats.
- Radar and Detection:
- Iran has developed indigenous radar systems capable of tracking various missile types. Effective early detection is critical for timely interception.
Challenges in Effectiveness
- Advanced Israeli Technology:
- Israeli missiles often incorporate stealth technology and advanced guidance systems, which can complicate interception efforts.
- Geopolitical Dynamics:
- In a conflict scenario, Israel’s air force may use tactics to overwhelm air defenses, such as launching multiple missiles simultaneously or using decoys.
- Response Time:
- The speed and trajectory of incoming missiles can significantly impact the ability of Iran’s systems to respond effectively.
- Operational Readiness:
- The effectiveness of Iran’s air defense systems depends on their operational status and the training of personnel to handle complex scenarios.
Historical Context
In past conflicts, Iran has claimed successes in intercepting drones and missiles. However, the real-world effectiveness against a comprehensive Israeli missile assault remains uncertain and would likely depend on numerous tactical and technological factors.
Conclusion
While Iran’s air defense systems have capabilities that could potentially defend against missile attacks from Israel, several challenges, including advanced enemy technology and tactics, could limit their effectiveness. The situation remains complex and fluid, with ongoing developments in both countries’ military capabilities.
What are Iran’s primary air defense systems?
Iran’s primary systems include Bavar-373, Khordad 15, and the S-300, designed to intercept various aerial threats.
How effective are these systems against Israeli missiles?
They provide a layered defense, but challenges remain due to advanced Israeli missile technology and tactics.
What is the range of the Bavar-373 system?
The Bavar-373 has a range of up to 200 km for intercepting aerial threats.
Can Iran’s air defense intercept drones?
Yes, Iran’s systems are designed to detect and intercept drones, which are part of the missile threat spectrum.
What role does radar play in Iran’s defense?
Advanced radar systems are crucial for early detection and tracking of incoming missiles.
What challenges does Iran face in missile defense?
Challenges include the speed of incoming missiles, Israeli stealth technology, and the need for rapid response.